
Parallel Analysis of RNA and Protein Expression Using SingleShot™ Cell Culture Lysates
Comprehensive and effective gene expression studies evaluate both transcriptional and translational regulation. A streamlined protocol was developed for the parallel analysis of mRNA and protein levels using a single lysate produced from cultured cells.

From Optimization to Automation: Multidimensional (Multi-D) Histidine-Tag Protein Purification
A well-designed multidimensional (Multi-D) chromatography process, which utilizes optimized individual column methods, can help automate multistep protein purification processes. This can help you save time and increase productivity. See how you can use Multi-D chromatography to expedite the purification of polyhistidine-tagged proteins when using a typical capture, intermediate, and polish purification workflow.

Mixed-Mode Chromatography for mAb S Aggregate Removal: Comparison of CHT™ Ceramic Hydroxyapatite, Capto adhere, and Capto adhere ImpRes
The separation of monomers from product-related impurities is quite challenging in process separations. It requires a thorough screening and an efficient resin to get efficiency in the purification process. Review the performance data of Bio-Rad’s mixed mode CHT™ Ceramic Hydroxapatite in achieving process separation efficiency and how it compares with various Capto media.

A Semi-Automated Quantitative PCR Approach to Assess Differential Anti-Apoptotic Gene Expression Patterns Associated with Prostate Cancer Progression
Gene expression analyses become complicated and extremely time consuming when large numbers of genes need to be analyzed. Here we present a semi-automated qPCR workflow with reduced setup and processing times using Bio-Rad’s PrimePCR™ Panels and CFX Automation System II Plate Handler.

Ultra-Sensitive Quantification of Genome Editing Events Using Droplet Digital PCR
Genome editing using tools such as CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN has gained enormous popularity in recent days due to their ability to create precise deletions or insertions. However when the frequency of these gene edits are really small, an ultrasensitive method like ddPCR™ is needed for accurate quantification. This technote explains how Droplet Digital™ PCR is used for the detection of HDR and NHEJ alleles generated using CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN editing systems.

Advantages of Multidimensional (Multi-D) Chromatography Using the NGC™ Chromatography System over Traditional Sequential Chromatography
Traditional sequential chromatography typically requires intensive hands-on user manipulation, which could hinder the reproducibility of protein purification runs. Multi-D chromatography aims to improve this process while maintaining the efficacy of the traditional workflow.
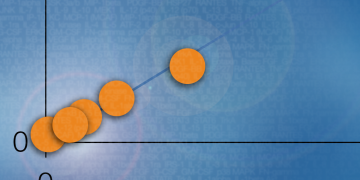
Bio-Plex Pro Human Inflammation Assays: Performance Data
Bio-Rad’s Bio-Plex Pro Human Inflammation Assay measures 37 of the most relevant inflammation biomarkers, including TNF superfamily proteins, Treg cytokines, IFN proteins, and matrix metalloproteinases, in a single multiplex panel.Check out the performance characteristics of the assay panel in this report.
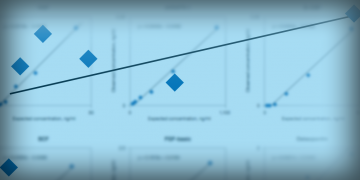
Cross-Reactivity of Bio-Plex Pro™ Human Cancer Biomarker Assays to Mouse Proteins
Mice are an optimal model organism for human cancer studies. However, when experiments involve a human xenograft in a mouse host, cross-reactivity presents a major concern in measuring biomarkers. This technical report evaluates 14 Bio-Plex Pro Human Cancer Biomarker Assays for cross reactivity to mouse proteins and discusses the resulting data.
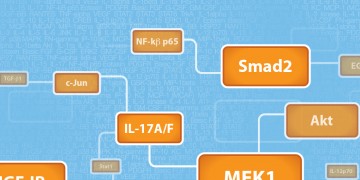
Multiplex Analysis of Cell Death Markers Using Bio-Plex Pro™ RBM Apoptosis Assays
Bio-Rad’s new Bio-Plex Pro RBM Apoptosis Multiplex Assays enable complex, quantitative analyses of biomarkers in the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Learn more about these biomarkers and view sample data and performance characteristics of these assays in this detailed technical report.

Better, Faster, and Less Expensive Gene Expression Analysis Using Multiplex One-Step RT-qPCR: A Case Study of Colorectal Cancer
Conducting a triplex one-step RT-qPCR assay promises a more efficient and economical analysis of gene expression compared to running three individual assays. This technical report describes a colorectal cancer case study where a triplex multiplex assay was validated.
